Troubleshooting electronic circuits is both a science and an art. While theory provides the foundation, real-world diagnostics require methodical thinking, accurate observation, and the right tools. Whether youre working on a vehicle, a PLC system, or a domestic device, the ability to locate faults efficiently depends on your understanding of how circuits behave under both normal and abnormal conditions. This Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram manualupdated for 2026 under http://wiringschema.comsummarizes the diagnostic procedures used by professionals in Belt Diagram and beyond.
The first step in any diagnostic process is **observation**. Before touching a single wire, take time to understand the symptoms. Is the circuit completely dead, or does it behave intermittently? Does a fuse blow repeatedly, or does a component operate erratically? Each clue helps narrow down the possibilities. Skilled technicians gather this information before physical testing, because many electrical problems stem not from defective parts but from corrosion, vibration, or poor grounding.
Once symptoms are noted, the second step is **verification**. Always confirm the complaint. If a report says a light wont turn on, verify whether the issue lies in the bulb, switch, relay, or fuse. Use every sensesight, sound, touch, and even smellto identify signs of failure. Burn marks on insulation, a clicking relay, or the odor of overheated plastic may point directly to the root cause. Observation is data, and data drives decisions.
Next comes **isolation of the circuit**. Divide large systems into smaller test sections and evaluate each separately. Begin at the power source and move toward the load, measuring voltage at each stage. A sudden voltage drop or missing reading shows that the fault exists between the last known good point and the next. This logical progression avoids random part swapping and pinpoints faults with precision.
Using proper **test equipment** is critical. A digital multimeter (DMM) is your universal instrument, allowing measurement of voltage, resistance, and continuity. However, a static reading of 12 volts doesnt guarantee healthvoltage under load matters more. Thats why professionals perform **voltage drop tests**, measuring potential difference across connectors or wires while current flows. Even a 0.5-volt drop can reveal hidden resistance, dirt, or oxidation that disrupts performance.
For advanced diagnostics, an **oscilloscope** becomes indispensable. It displays voltage as a waveform over time, revealing how sensors, data lines, and actuators behave dynamically. With it, you can verify if a PWM (pulse-width modulation) signal is clean, or if interference distorts communication. Mastering waveform reading takes practice, but it opens a window into the unseen world of electronic activitya skill every professional in Belt Diagram should learn.
**Continuity testing** verifies whether current can flow freely through a conductor. Its a quick way to check for breaks or bad joints, but its not absolute proof of circuit integrity. A wire can pass a low-current continuity test and still fail under load due to corrosion or poor crimping. Combine continuity checks with voltage drop measurements for a complete diagnostic profile.
**Ground testing** is equally vital. Many mysterious faults trace back to weak or rusty grounds. Loose bolts, paint between contacts, or overloaded return paths can mimic sensor or communication failures. To test, measure voltage drop between the components ground and the negative terminal while active. Any reading above **0.1 volts** signals excessive resistance. Cleaning and protecting ground points with dielectric grease prevents future recurrence.
In circuits using relays, solenoids, or motors, sometimes your **ears and hands** are diagnostic tools too. A relay might click but fail internally because of burned contacts. A motor that hums but doesnt spin could have power but insufficient torque due to mechanical binding or low voltage. Dont underestimate the simplicity of sensory checksthey often lead to quicker solutions than complex instruments.
Documentation is your greatest ally. Always consult **wiring diagrams** and schematics before testing. They show how circuits connect, where protection devices are located, and how current flows between sections. Comparing real-world readings to diagram expectations exposes faults instantly. Professionals treat schematics like roadmapsthey show direction, not just location, and help connect cause with effect.
An advanced yet cautious method is **substitution testing**replacing a suspected faulty component with a known-good one. If the issue disappears, the original part was bad. But use this only when confident, since swapping components in sensitive electronic systems can introduce new errors or damage.
Every diagnostic process concludes with **verification and prevention**. After a repair, always retest to confirm operation, then determine *why* the failure occurred. Was it mechanical wear, corrosion, overload, heat, or a design flaw? Taking preventive measuresrerouting wires, reinforcing insulation, tightening groundsprevents the same issue from returning.
Effective troubleshooting combines logic, observation, and technical understanding. Each measurement builds a clearer picture of circuit behavior. With experience, technicians develop whats known as *electrical intuition*the ability to sense where faults lie before testing. Its not guesswork; its experience guided by knowledge.
By following structured procedures as outlined in Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram, you transform trial-and-error into predictable, efficient diagnosis. Wiring diagrams stop being static imagesthey become **interactive maps of cause and effect**. In the end, the true skill of an electrical specialist isnt in changing parts; its in understanding how the system thinks, acts, and recovers. Thats the essence of professional troubleshootingmastered and shared globally through http://wiringschema.com in 2026, built upon decades of engineering expertise from Belt Diagram.
Electrical safety begins long before any tool touches the wire. Review the diagram and understand what voltage and current you’re dealing with. Disconnect the main source and attach a “Do Not Energize” tag. Never work alone when dealing with high-energy circuits. Proper lighting, dry surroundings, and a stable surface prevent most accidental injuries.
Handling techniques define the difference between a temporary repair and a lasting installation. Choose tools that match the cable size and provide insulation from live parts. Be careful not to notch the conductor while stripping, because that weak spot can arc or corrode. Route low-level signal wires far from heavy current cables to limit electromagnetic noise. Neat harness routing is not just cosmetic — it delivers durability and easier service.
After finishing, perform a continuity test and insulation-resistance check. Look for loose strands, cut jackets, or plugs that aren’t fully seated. Do not energize until all shields and covers are reattached. Safety is not paperwork; it’s a working habit that protects people and hardware.
Reading a schematic means watching information and power move, not just staring at lines. Symbols identify which blocks generate signals, which blocks sense conditions, and which blocks drive outputs. Whenever you see ECU drawn as a box with arrows, that’s the map of who is sending data in and which outputs it’s commanding out.
Those tiny tags on each arrow explain what kind of data is traveling. You’ll see TEMP SIG, SPD SIG, POS FBK (position feedback), CMD OUT, PWM DRV — each describes a different role. Without those labels, you couldn’t tell if that pin is for sensing or commanding in “Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram”.
This matters for probe safety in Belt Diagram. If a pin is marked SENSOR IN you do not drive it; if it’s DRV OUT you don’t backfeed it because it’s already a driver. Reading those tags first stops you from backfeeding a controller in 2026, protects liability for http://wiringschema.com, and leaves proof in https://http://wiringschema.com/chevy-454-engine-belt-diagram/WIRINGSCHEMA.COM of what was accessed.

Wire color standards exist so that technicians share a common understanding when reading or building circuits. {Each region or manufacturer may apply slight variations, but the principles remain universal — colors identify function.|Though manufacturers may vary, colors still represent consistent meanings acro...
In Belt Diagram, the automotive and industrial wiring standards often follow the ISO and IEC norms. {Brown, black, or blue typically denote grounded or neutral conductors, while red, yellow, or white indicate energized circuits.|Ground or neutral wires are generally brown, black, or blue, while live or switched feeds are red, y...
Before you begin any repair in “Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram”, consult the service manual for exact color definitions. {Manufacturers sometimes repurpose wire colors for secondary circuits, so blind assumptions can create faults or safety hazards in 2026.|Occasionally, manufacturers reuse certain colors for sub-circuits, and guessing their r...

Power distribution acts as the structured system that directs energy from the source to all connected circuits.
It ensures that voltage remains consistent, current stays balanced, and all components in “Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram” operate safely under load.
Without effective distribution design, electrical networks can experience overload, high resistance, or unexpected equipment shutdowns.
A properly managed layout keeps power steady, reduces losses, and protects sensitive components from electrical stress.
In short, power distribution is the invisible structure that guarantees operational safety and system reliability.
Designing an efficient power distribution network requires a deep understanding of circuit behavior and load flow.
Every cable and component must be chosen according to its capacity and environmental tolerance.
Within Belt Diagram, these international standards help engineers maintain reliability and regulatory compliance.
Power and signal lines should be separated to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and maintain data accuracy.
All fuses and ground terminals must be located conveniently and designed for durability.
Following these guidelines ensures “Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram” maintains consistent operation in challenging electrical conditions.
After setup, verification ensures that every circuit performs according to design expectations.
Technicians must check circuit continuity, grounding integrity, and voltage stability under various conditions.
Any updates or wiring modifications must be reflected in both the printed schematic and digital documentation.
Voltage readings, inspection photos, and maintenance records should be stored safely in http://wiringschema.com for future access.
Attaching 2026 and https://http://wiringschema.com/chevy-454-engine-belt-diagram/WIRINGSCHEMA.COM provides complete documentation history and traceability.
By combining design precision, safety testing, and documentation, “Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram” achieves durable, stable, and long-term power integrity.

Grounding is a crucial safety principle that forms the basis of every reliable electrical installation.
It provides a low-resistance connection to the earth, allowing excess current to flow safely during fault conditions.
Without grounding, “Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram” may experience high-voltage buildup, system instability, or even electric shock hazards.
Proper grounding allows safe discharge of electrical faults, smooth voltage levels, and consistent system performance.
In Belt Diagram, grounding is a legal and engineering standard required for all power and communication systems.
Designing grounding begins with studying soil type, current distribution, and weather conditions.
Each connection needs to be durable, rust-resistant, and structurally strong for long-term reliability.
Across Belt Diagram, IEC 60364 and IEEE 142 outline standard grounding methods used for design and testing.
Ground wires must have the right thickness to handle current safely and reduce voltage drop.
All equipment frames and metallic structures should be connected to a single grounding grid to ensure potential equalization.
By applying these principles, “Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram” achieves safety, stability, and long-term system performance.
Continuous maintenance ensures long-term grounding reliability and compliance.
Technicians should check grounding continuity, test resistance levels, and document any changes or repairs.
Any sign of corrosion must be repaired quickly and followed by a resistance recheck.
Maintenance data and testing records should be archived to meet compliance and inspection standards.
Grounding systems should be tested once each 2026 or after significant equipment updates.
Through proper maintenance and monitoring, “Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram” guarantees electrical safety and long-lasting reliability.
Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram Wiring Guide – Connector Index & Pinout Reference 2026
Automotive systems use many types of connectors that vary in size, locking style, and pin count. Each design serves the purpose of maintaining safe and reliable current flow. They range from small sensor plugs to large ECU couplings that carry critical control signals.
Inline connectors are commonly used to link two harness sections and are often sealed with rubber grommets for water resistance. Complex multi-pin connectors reduce wiring clutter and simplify maintenance. Terminal block connectors handle higher current loads, while sensor connectors use compact housings to minimize interference.
Locking tabs and keyed housings make sure connectors can only fit one way. By recognizing the design elements of each connector, technicians maintain harness accuracy. Understanding connector categories prevents wiring faults and extends harness life.

Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram Full Manual – Sensor Inputs 2026
The Brake Pedal Position (BPP) sensor detects the movement and position of the brake pedal. {When the pedal is pressed, the sensor changes its resistance or voltage output.|The ECU uses this information to trigger braking-related functions and system coordination.|Accurate BPP data ensures immediate response ...
Potentiometer types vary voltage according to pedal movement, while Hall-effect sensors output digital on/off or pulse signals. {Some advanced systems use dual-circuit sensors for redundancy and fail-safe operation.|Dual outputs allow comparison between channels for error detection.|This redundancy improves reliability in safety-critical...
Common symptoms of a faulty BPP sensor include stuck brake lights, warning codes, or disabled cruise control. {Maintaining BPP sensor function ensures safety compliance and reliable braking communication.|Proper calibration prevents misinterpretation of brake input by the control unit.|Understanding BPP sensor feedback enhances diagnostic pre...

Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram Full Manual – Actuator Outputs 2026
Solenoid actuators provide fast, precise control for fuel, hydraulic, and pneumatic systems. When current flows through the coil, it pulls or pushes a metal rod depending on design.
Solenoid circuits are typically controlled using transistors or driver modules to handle high current. Protective diodes or snubber circuits are included to prevent voltage spikes caused by coil de-energization.
Inspect wiring, connectors, and driver circuits for signs of overheating or corrosion. Knowledge of solenoid control is vital for maintaining accuracy and safety in modern systems.

Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram Full Manual – Actuator Outputs Reference 2026
An EGR actuator reduces emissions by directing part of exhaust gases back into the intake system. {The EGR valve opens or closes according to ECU commands, adjusting based on engine load and speed.|Modern systems use electric or vacuum-operated actuators to regulate exhaust flow.|Electric EGR valves use st...
Position feedback sensors ensure the ECU knows the exact opening percentage. Calibration is crucial to prevent engine hesitation or stalling due to incorrect exhaust ratio.
Carbon buildup inside the EGR valve is a common failure cause. Understanding actuator operation in EGR systems helps technicians ensure compliance with emission standards.

Communication bus systems in Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram serve as the
coordinated digital backbone that links sensors, actuators, and
electronic control units into a synchronized data environment. Through
structured packet transmission, these networks maintain consistency
across powertrain, chassis, and body domains even under demanding
operating conditions such as thermal expansion, vibration, and
high-speed load transitions.
High-speed CAN governs engine timing, ABS
logic, traction strategies, and other subsystems that require real-time
message exchange, while LIN handles switches and comfort electronics.
FlexRay supports chassis-level precision, and Ethernet transports camera
and radar data with minimal latency.
Technicians often
identify root causes such as thermal cycling, micro-fractured
conductors, or grounding imbalances that disrupt stable signaling.
Careful inspection of routing, shielding continuity, and connector
integrity restores communication reliability.

Fuse‑relay networks
are engineered as frontline safety components that absorb electrical
anomalies long before they compromise essential subsystems. Through
measured response rates and calibrated cutoff thresholds, they ensure
that power surges, short circuits, and intermittent faults remain
contained within predefined zones. This design philosophy prevents
chain‑reaction failures across distributed ECUs.
In modern architectures, relays handle repetitive activation
cycles, executing commands triggered by sensors or control software.
Their isolation capabilities reduce stress on low‑current circuits,
while fuses provide sacrificial protection whenever load spikes exceed
tolerance thresholds. Together they create a multi‑layer defense grid
adaptable to varying thermal and voltage demands.
Technicians often
diagnose issues by tracking inconsistent current delivery, noisy relay
actuation, unusual voltage fluctuations, or thermal discoloration on
fuse panels. Addressing these problems involves cleaning terminals,
reseating connectors, conditioning ground paths, and confirming load
consumption through controlled testing. Maintaining relay responsiveness
and fuse integrity ensures long‑term electrical stability.

Test points play a foundational role in Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram by
providing regulated reference rails distributed across the electrical
network. These predefined access nodes allow technicians to capture
stable readings without dismantling complex harness assemblies. By
exposing regulated supply rails, clean ground paths, and buffered signal
channels, test points simplify fault isolation and reduce diagnostic
time when tracking voltage drops, miscommunication between modules, or
irregular load behavior.
Technicians rely on these access nodes to conduct regulated reference
rails, waveform pattern checks, and signal-shape verification across
multiple operational domains. By comparing known reference values
against observed readings, inconsistencies can quickly reveal poor
grounding, voltage imbalance, or early-stage conductor fatigue. These
cross-checks are essential when diagnosing sporadic faults that only
appear during thermal expansion cycles or variable-load driving
conditions.
Common issues identified through test point evaluation include voltage
fluctuation, unstable ground return, communication dropouts, and erratic
sensor baselines. These symptoms often arise from corrosion, damaged
conductors, poorly crimped terminals, or EMI contamination along
high-frequency lines. Proper analysis requires oscilloscope tracing,
continuity testing, and resistance indexing to compare expected values
with real-time data.

Measurement procedures for Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram begin with baseline
voltage validation to establish accurate diagnostic foundations.
Technicians validate stable reference points such as regulator outputs,
ground planes, and sensor baselines before proceeding with deeper
analysis. This ensures reliable interpretation of electrical behavior
under different load and temperature conditions.
Technicians utilize these measurements to evaluate waveform stability,
baseline voltage validation, and voltage behavior across multiple
subsystem domains. Comparing measured values against specifications
helps identify root causes such as component drift, grounding
inconsistencies, or load-induced fluctuations.
Common measurement findings include fluctuating supply rails, irregular
ground returns, unstable sensor signals, and waveform distortion caused
by EMI contamination. Technicians use oscilloscopes, multimeters, and
load probes to isolate these anomalies with precision.

Troubleshooting for Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram begins with macro-level
diagnostic initiation, ensuring the diagnostic process starts with
clarity and consistency. By checking basic system readiness, technicians
avoid deeper misinterpretations.
Field testing
incorporates resistive drift characterization, providing insight into
conditions that may not appear during bench testing. This highlights
environment‑dependent anomalies.
Poorly-seated grounds cause abrupt changes in
sensor reference levels, disturbing ECU logic. Systematic ground‑path
verification isolates the unstable anchor point.
Across diverse vehicle
architectures, issues related to moisture intrusion causing transient
shorts in junction boxes represent a dominant source of unpredictable
faults. These faults may develop gradually over months of thermal
cycling, vibrations, or load variations, ultimately causing operational
anomalies that mimic unrelated failures. Effective troubleshooting
requires technicians to start with a holistic overview of subsystem
behavior, forming accurate expectations about what healthy signals
should look like before proceeding.
Patterns
linked to moisture intrusion causing transient shorts in junction boxes
frequently reveal themselves during active subsystem transitions, such
as ignition events, relay switching, or electronic module
initialization. The resulting irregularities—whether sudden voltage
dips, digital noise pulses, or inconsistent ground offset—are best
analyzed using waveform-capture tools that expose micro-level
distortions invisible to simple multimeter checks.
Left unresolved, moisture
intrusion causing transient shorts in junction boxes may cause cascading
failures as modules attempt to compensate for distorted data streams.
This can trigger false DTCs, unpredictable load behavior, delayed
actuator response, and even safety-feature interruptions. Comprehensive
analysis requires reviewing subsystem interaction maps, recreating
stress conditions, and validating each reference point’s consistency
under both static and dynamic operating states.
For
long-term system stability, effective electrical upkeep prioritizes
long-term wiring lifecycle preservation, allowing technicians to
maintain predictable performance across voltage-sensitive components.
Regular inspections of wiring runs, connector housings, and grounding
anchors help reveal early indicators of degradation before they escalate
into system-wide inconsistencies.
Addressing concerns tied to long-term wiring lifecycle preservation
involves measuring voltage profiles, checking ground offsets, and
evaluating how wiring behaves under thermal load. Technicians also
review terminal retention to ensure secure electrical contact while
preventing micro-arcing events. These steps safeguard signal clarity and
reduce the likelihood of intermittent open circuits.
Failure
to maintain long-term wiring lifecycle preservation can lead to
cascading electrical inconsistencies, including voltage drops, sensor
signal distortion, and sporadic subsystem instability. Long-term
reliability requires careful documentation, periodic connector service,
and verification of each branch circuit’s mechanical and electrical
health under both static and dynamic conditions.
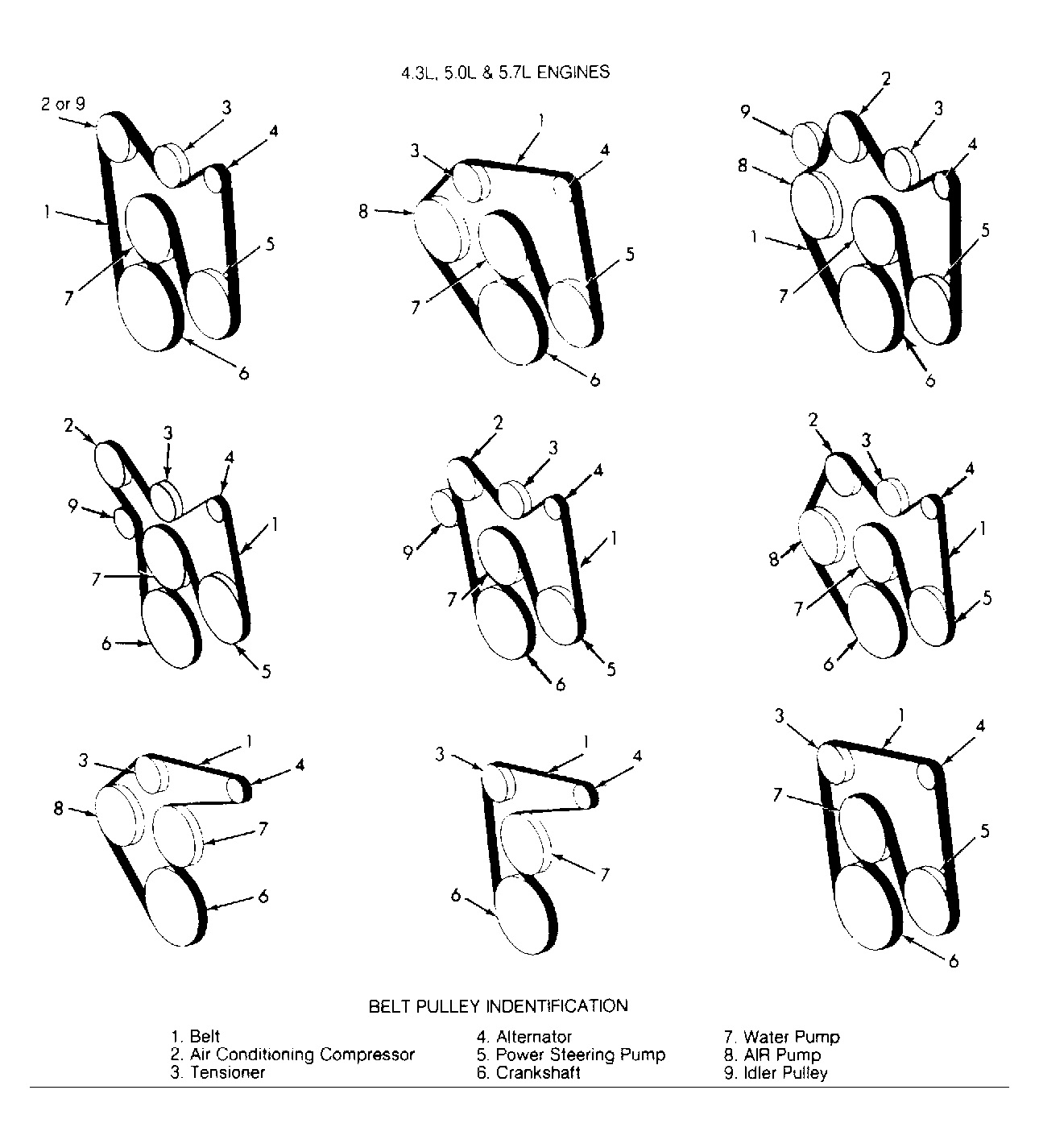
The appendix for Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram serves as a consolidated
reference hub focused on connector family classification and labeling
consistency, offering technicians consistent terminology and structured
documentation practices. By collecting technical descriptors,
abbreviations, and classification rules into a single section, the
appendix streamlines interpretation of wiring layouts across diverse
platforms. This ensures that even complex circuit structures remain
approachable through standardized definitions and reference cues.
Documentation related to connector family classification and labeling
consistency frequently includes structured tables, indexing lists, and
lookup summaries that reduce the need to cross‑reference multiple
sources during system evaluation. These entries typically describe
connector types, circuit categories, subsystem identifiers, and signal
behavior definitions. By keeping these details accessible, technicians
can accelerate the interpretation of wiring diagrams and troubleshoot
with greater accuracy.
Robust appendix material for connector
family classification and labeling consistency strengthens system
coherence by standardizing definitions across numerous technical
documents. This reduces ambiguity, supports proper cataloging of new
components, and helps technicians avoid misinterpretation that could
arise from inconsistent reference structures.
Deep analysis of signal integrity in Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram requires
investigating how frequency-domain interference impacting ECU logic
disrupts expected waveform performance across interconnected circuits.
As signals propagate through long harnesses, subtle distortions
accumulate due to impedance shifts, parasitic capacitance, and external
electromagnetic stress. This foundational assessment enables technicians
to understand where integrity loss begins and how it
evolves.
When frequency-domain interference impacting ECU logic occurs, signals
may experience phase delays, amplitude decay, or transient ringing
depending on harness composition and environmental exposure. Technicians
must review waveform transitions under varying thermal, load, and EMI
conditions. Tools such as high‑bandwidth oscilloscopes and frequency
analyzers reveal distortion patterns that remain hidden during static
measurements.
If frequency-domain
interference impacting ECU logic persists, cascading instability may
arise: intermittent communication, corrupt data frames, or erratic
control logic. Mitigation requires strengthening shielding layers,
rebalancing grounding networks, refining harness layout, and applying
proper termination strategies. These corrective steps restore signal
coherence under EMC stress.
Advanced EMC evaluation in Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram requires close
study of voltage droop recovery delays in transient events, a phenomenon
that can significantly compromise waveform predictability. As systems
scale toward higher bandwidth and greater sensitivity, minor deviations
in signal symmetry or reference alignment become amplified.
Understanding the initial conditions that trigger these distortions
allows technicians to anticipate system vulnerabilities before they
escalate.
When voltage droop recovery delays in transient events is present, it
may introduce waveform skew, in-band noise, or pulse deformation that
impacts the accuracy of both analog and digital subsystems. Technicians
must examine behavior under load, evaluate the impact of switching
events, and compare multi-frequency responses. High‑resolution
oscilloscopes and field probes reveal distortion patterns hidden in
time-domain measurements.
If left unresolved, voltage droop recovery delays in
transient events may trigger cascading disruptions including frame
corruption, false sensor readings, and irregular module coordination.
Effective countermeasures include controlled grounding, noise‑filter
deployment, re‑termination of critical paths, and restructuring of cable
routing to minimize electromagnetic coupling.

A comprehensive
assessment of waveform stability requires understanding the effects of
conducted surges from auxiliary accessories disrupting ECU timing, a
factor capable of reshaping digital and analog signal profiles in subtle
yet impactful ways. This initial analysis phase helps technicians
identify whether distortions originate from physical harness geometry,
electromagnetic ingress, or internal module reference instability.
When conducted surges from auxiliary accessories disrupting ECU timing
is active within a vehicle’s electrical environment, technicians may
observe shift in waveform symmetry, rising-edge deformation, or delays
in digital line arbitration. These behaviors require examination under
multiple load states, including ignition operation, actuator cycling,
and high-frequency interference conditions. High-bandwidth oscilloscopes
and calibrated field probes reveal the hidden nature of such
distortions.
If
unchecked, conducted surges from auxiliary accessories disrupting ECU
timing can escalate into broader electrical instability, causing
corruption of data frames, synchronization loss between modules, and
unpredictable actuator behavior. Effective corrective action requires
ground isolation improvements, controlled harness rerouting, adaptive
termination practices, and installation of noise-suppression elements
tailored to the affected frequency range.

Evaluating advanced signal‑integrity interactions involves
examining the influence of ground-collapse instability under combined
thermal and EMI stress, a phenomenon capable of inducing significant
waveform displacement. These disruptions often develop gradually,
becoming noticeable only when communication reliability begins to drift
or subsystem timing loses coherence.
When ground-collapse instability under combined thermal and EMI stress
is active, waveform distortion may manifest through amplitude
instability, reference drift, unexpected ringing artifacts, or shifting
propagation delays. These effects often correlate with subsystem
transitions, thermal cycles, actuator bursts, or environmental EMI
fluctuations. High‑bandwidth test equipment reveals the microscopic
deviations hidden within normal signal envelopes.
If unresolved, ground-collapse instability
under combined thermal and EMI stress may escalate into severe
operational instability, corrupting digital frames or disrupting
tight‑timing control loops. Effective mitigation requires targeted
filtering, optimized termination schemes, strategic rerouting, and
harmonic suppression tailored to the affected frequency bands.

Advanced waveform diagnostics in Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram must account
for PWM-driven magnetic noise violating analog threshold margins, a
complex interaction that reshapes both analog and digital signal
behavior across interconnected subsystems. As modern vehicle
architectures push higher data rates and consolidate multiple electrical
domains, even small EMI vectors can distort timing, amplitude, and
reference stability.
Systems exposed to PWM-driven magnetic noise violating
analog threshold margins often show instability during rapid subsystem
transitions. This instability results from interference coupling into
sensitive wiring paths, causing skew, jitter, or frame corruption.
Multi-domain waveform capture reveals how these disturbances propagate
and interact.
Long-term exposure to PWM-driven magnetic noise violating analog
threshold margins can lead to cumulative communication degradation,
sporadic module resets, arbitration errors, and inconsistent sensor
behavior. Technicians mitigate these issues through grounding
rebalancing, shielding reinforcement, optimized routing, precision
termination, and strategic filtering tailored to affected frequency
bands.
This section on STARTING/CHARGING explains how these principles apply to 454 engine belt diagram systems. Focus on repeatable tests, clear documentation, and safe handling. Keep a simple log: symptom → test → reading → decision → fix.

Harness Layout Variant #2 for Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram focuses on
electrical separation rules for hybrid high-voltage and low-voltage
harnesses, a structural and electrical consideration that influences
both reliability and long-term stability. As modern vehicles integrate
more electronic modules, routing strategies must balance physical
constraints with the need for predictable signal behavior.
During refinement, electrical separation rules for hybrid high-voltage
and low-voltage harnesses impacts EMI susceptibility, heat distribution,
vibration loading, and ground continuity. Designers analyze spacing,
elevation changes, shielding alignment, tie-point positioning, and path
curvature to ensure the harness resists mechanical fatigue while
maintaining electrical integrity.
If neglected, electrical separation rules for hybrid high-voltage
and low-voltage harnesses may cause abrasion, insulation damage,
intermittent electrical noise, or alignment stress on connectors.
Precision anchoring, balanced tensioning, and correct separation
distances significantly reduce such failure risks across the vehicle’s
entire electrical architecture.

Harness Layout Variant #3 for Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram focuses on
high-integrity routing lanes for advanced driver‑assist modules, an
essential structural and functional element that affects reliability
across multiple vehicle zones. Modern platforms require routing that
accommodates mechanical constraints while sustaining consistent
electrical behavior and long-term durability.
In real-world
operation, high-integrity routing lanes for advanced driver‑assist
modules determines how the harness responds to thermal cycling, chassis
motion, subsystem vibration, and environmental elements. Proper
connector staging, strategic bundling, and controlled curvature help
maintain stable performance even in aggressive duty cycles.
If not
addressed, high-integrity routing lanes for advanced driver‑assist
modules may lead to premature insulation wear, abrasion hotspots,
intermittent electrical noise, or connector fatigue. Balanced
tensioning, routing symmetry, and strategic material selection
significantly mitigate these risks across all major vehicle subsystems.

The architectural
approach for this variant prioritizes trailer-harness detachment safeguards and service loops, focusing on
service access, electrical noise reduction, and long-term durability. Engineers balance bundle compactness
with proper signal separation to avoid EMI coupling while keeping the routing footprint efficient.
In real-world operation,
trailer-harness detachment safeguards and service loops affects signal quality near actuators, motors, and
infotainment modules. Cable elevation, branch sequencing, and anti-chafe barriers reduce premature wear. A
combination of elastic tie-points, protective sleeves, and low-profile clips keeps bundles orderly yet
flexible under dynamic loads.
If
overlooked, trailer-harness detachment safeguards and service loops may lead to insulation wear, loose
connections, or intermittent signal faults caused by chafing. Solutions include anchor repositioning, spacing
corrections, added shielding, and branch restructuring to shorten paths and improve long-term serviceability.
The initial stage of Diagnostic
Flowchart #1 emphasizes flow‑based confirmation of analog signal drift sources, ensuring that the most
foundational electrical references are validated before branching into deeper subsystem evaluation. This
reduces misdirection caused by surface‑level symptoms. Mid‑stage analysis integrates flow‑based
confirmation of analog signal drift sources into a structured decision tree, allowing each measurement to
eliminate specific classes of faults. By progressively narrowing the fault domain, the technician accelerates
isolation of underlying issues such as inconsistent module timing, weak grounds, or intermittent sensor
behavior. If flow‑based confirmation of analog signal drift sources is not
thoroughly validated, subtle faults can cascade into widespread subsystem instability. Reinforcing each
decision node with targeted measurements improves long‑term reliability and prevents misdiagnosis.
Diagnostic Flowchart #2 for Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram begins by addressing real-time voltage ripple mapping
across control clusters, establishing a clear entry point for isolating electrical irregularities that may
appear intermittent or load‑dependent. Technicians rely on this structured starting node to avoid
misinterpretation of symptoms caused by secondary effects. As the diagnostic flow advances, real-time
voltage ripple mapping across control clusters shapes the logic of each decision node. Mid‑stage evaluation
involves segmenting power, ground, communication, and actuation pathways to progressively narrow down fault
origins. This stepwise refinement is crucial for revealing timing‑related and load‑sensitive
anomalies. Completing the flow ensures that real-time voltage ripple mapping across control
clusters is validated under multiple operating conditions, reducing the likelihood of recurring issues. The
resulting diagnostic trail provides traceable documentation that improves future troubleshooting accuracy.
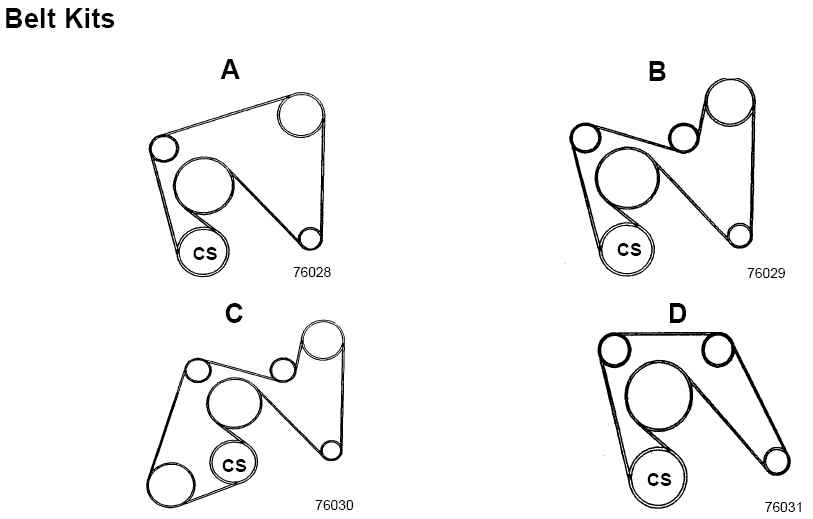
Diagnostic Flowchart #3 for Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram initiates with thermal‑dependent CAN dropout
reproduction, establishing a strategic entry point for technicians to separate primary electrical faults from
secondary symptoms. By evaluating the system from a structured baseline, the diagnostic process becomes far
more efficient. Throughout the analysis, thermal‑dependent CAN dropout
reproduction interacts with branching decision logic tied to grounding stability, module synchronization, and
sensor referencing. Each step narrows the diagnostic window, improving root‑cause accuracy. Once
thermal‑dependent CAN dropout reproduction is fully evaluated across multiple load states, the technician can
confirm or dismiss entire fault categories. This structured approach enhances long‑term reliability and
reduces repeat troubleshooting visits.

Diagnostic Flowchart
#4 for Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram focuses on controlled reproduction of temperature‑dependent dropouts, laying
the foundation for a structured fault‑isolation path that eliminates guesswork and reduces unnecessary
component swapping. The first stage examines core references, voltage stability, and baseline communication
health to determine whether the issue originates in the primary network layer or in a secondary subsystem.
Technicians follow a branched decision flow that evaluates signal symmetry, grounding patterns, and frame
stability before advancing into deeper diagnostic layers. As the evaluation continues, controlled
reproduction of temperature‑dependent dropouts becomes the controlling factor for mid‑level branch decisions.
This includes correlating waveform alignment, identifying momentary desync signatures, and interpreting module
wake‑timing conflicts. By dividing the diagnostic pathway into focused electrical domains—power delivery,
grounding integrity, communication architecture, and actuator response—the flowchart ensures that each stage
removes entire categories of faults with minimal overlap. This structured segmentation accelerates
troubleshooting and increases diagnostic precision. The final stage ensures that controlled reproduction of temperature‑dependent dropouts is
validated under multiple operating conditions, including thermal stress, load spikes, vibration, and state
transitions. These controlled stress points help reveal hidden instabilities that may not appear during static
testing. Completing all verification nodes ensures long‑term stability, reducing the likelihood of recurring
issues and enabling technicians to document clear, repeatable steps for future diagnostics.

Case Study #1 for Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram examines a real‑world failure involving relay chatter produced by
marginal coil voltage under thermal load. The issue first appeared as an intermittent symptom that did not
trigger a consistent fault code, causing technicians to suspect unrelated components. Early observations
highlighted irregular electrical behavior, such as momentary signal distortion, delayed module responses, or
fluctuating reference values. These symptoms tended to surface under specific thermal, vibration, or load
conditions, making replication difficult during static diagnostic tests. Further investigation into relay
chatter produced by marginal coil voltage under thermal load required systematic measurement across power
distribution paths, grounding nodes, and communication channels. Technicians used targeted diagnostic
flowcharts to isolate variables such as voltage drop, EMI exposure, timing skew, and subsystem
desynchronization. By reproducing the fault under controlled conditions—applying heat, inducing vibration, or
simulating high load—they identified the precise moment the failure manifested. This structured process
eliminated multiple potential contributors, narrowing the fault domain to a specific harness segment,
component group, or module logic pathway. The confirmed cause tied to relay chatter produced by marginal coil
voltage under thermal load allowed technicians to implement the correct repair, whether through component
replacement, harness restoration, recalibration, or module reprogramming. After corrective action, the system
was subjected to repeated verification cycles to ensure long‑term stability under all operating conditions.
Documenting the failure pattern and diagnostic sequence provided valuable reference material for similar
future cases, reducing diagnostic time and preventing unnecessary part replacement.

Case Study #2 for Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram examines a real‑world failure involving sensor contamination
leading to non‑linear analog output distortion. The issue presented itself with intermittent symptoms that
varied depending on temperature, load, or vehicle motion. Technicians initially observed irregular system
responses, inconsistent sensor readings, or sporadic communication drops. Because the symptoms did not follow
a predictable pattern, early attempts at replication were unsuccessful, leading to misleading assumptions
about unrelated subsystems. A detailed investigation into sensor contamination leading to non‑linear analog
output distortion required structured diagnostic branching that isolated power delivery, ground stability,
communication timing, and sensor integrity. Using controlled diagnostic tools, technicians applied thermal
load, vibration, and staged electrical demand to recreate the failure in a measurable environment. Progressive
elimination of subsystem groups—ECUs, harness segments, reference points, and actuator pathways—helped reveal
how the failure manifested only under specific operating thresholds. This systematic breakdown prevented
misdiagnosis and reduced unnecessary component swaps. Once the cause linked to sensor contamination leading
to non‑linear analog output distortion was confirmed, the corrective action involved either reconditioning the
harness, replacing the affected component, reprogramming module firmware, or adjusting calibration parameters.
Post‑repair validation cycles were performed under varied conditions to ensure long‑term reliability and
prevent future recurrence. Documentation of the failure characteristics, diagnostic sequence, and final
resolution now serves as a reference for addressing similar complex faults more efficiently.

Case Study #3 for Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram focuses on a real‑world failure involving vibration‑induced
intermittent open circuit within a high‑load harness branch. Technicians first observed erratic system
behavior, including fluctuating sensor values, delayed control responses, and sporadic communication warnings.
These symptoms appeared inconsistently, often only under specific temperature, load, or vibration conditions.
Early troubleshooting attempts failed to replicate the issue reliably, creating the impression of multiple
unrelated subsystem faults rather than a single root cause. To investigate vibration‑induced intermittent
open circuit within a high‑load harness branch, a structured diagnostic approach was essential. Technicians
conducted staged power and ground validation, followed by controlled stress testing that included thermal
loading, vibration simulation, and alternating electrical demand. This method helped reveal the precise
operational threshold at which the failure manifested. By isolating system domains—communication networks,
power rails, grounding nodes, and actuator pathways—the diagnostic team progressively eliminated misleading
symptoms and narrowed the problem to a specific failure mechanism. After identifying the underlying cause
tied to vibration‑induced intermittent open circuit within a high‑load harness branch, technicians carried out
targeted corrective actions such as replacing compromised components, restoring harness integrity, updating
ECU firmware, or recalibrating affected subsystems. Post‑repair validation cycles confirmed stable performance
across all operating conditions. The documented diagnostic path and resolution now serve as a repeatable
reference for addressing similar failures with greater speed and accuracy.

Case Study #4 for Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram examines a high‑complexity real‑world failure involving relay coil
desaturation during rapid thermal cycling causing unpredictable switching. The issue manifested across
multiple subsystems simultaneously, creating an array of misleading symptoms ranging from inconsistent module
responses to distorted sensor feedback and intermittent communication warnings. Initial diagnostics were
inconclusive due to the fault’s dependency on vibration, thermal shifts, or rapid load changes. These
fluctuating conditions allowed the failure to remain dormant during static testing, pushing technicians to
explore deeper system interactions that extended beyond conventional troubleshooting frameworks. To
investigate relay coil desaturation during rapid thermal cycling causing unpredictable switching, technicians
implemented a layered diagnostic workflow combining power‑rail monitoring, ground‑path validation, EMI
tracing, and logic‑layer analysis. Stress tests were applied in controlled sequences to recreate the precise
environment in which the instability surfaced—often requiring synchronized heat, vibration, and electrical
load modulation. By isolating communication domains, verifying timing thresholds, and comparing analog sensor
behavior under dynamic conditions, the diagnostic team uncovered subtle inconsistencies that pointed toward
deeper system‑level interactions rather than isolated component faults. After confirming the root mechanism
tied to relay coil desaturation during rapid thermal cycling causing unpredictable switching, corrective
action involved component replacement, harness reconditioning, ground‑plane reinforcement, or ECU firmware
restructuring depending on the failure’s nature. Technicians performed post‑repair endurance tests that
included repeated thermal cycling, vibration exposure, and electrical stress to guarantee long‑term system
stability. Thorough documentation of the analysis method, failure pattern, and final resolution now serves as
a highly valuable reference for identifying and mitigating similar high‑complexity failures in the future.

Case Study #5 for Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram investigates a complex real‑world failure involving PWM carrier
interference creating actuator response instability. The issue initially presented as an inconsistent mixture
of delayed system reactions, irregular sensor values, and sporadic communication disruptions. These events
tended to appear under dynamic operational conditions—such as elevated temperatures, sudden load transitions,
or mechanical vibration—which made early replication attempts unreliable. Technicians encountered symptoms
occurring across multiple modules simultaneously, suggesting a deeper systemic interaction rather than a
single isolated component failure. During the investigation of PWM carrier interference creating actuator
response instability, a multi‑layered diagnostic workflow was deployed. Technicians performed sequential
power‑rail mapping, ground‑plane verification, and high‑frequency noise tracing to detect hidden
instabilities. Controlled stress testing—including targeted heat application, induced vibration, and variable
load modulation—was carried out to reproduce the failure consistently. The team methodically isolated
subsystem domains such as communication networks, analog sensor paths, actuator control logic, and module
synchronization timing. This progressive elimination approach identified critical operational thresholds where
the failure reliably emerged. After determining the underlying mechanism tied to PWM carrier interference
creating actuator response instability, technicians carried out corrective actions that ranged from harness
reconditioning and connector reinforcement to firmware restructuring and recalibration of affected modules.
Post‑repair validation involved repeated cycles of vibration, thermal stress, and voltage fluctuation to
ensure long‑term stability and eliminate the possibility of recurrence. The documented resolution pathway now
serves as an advanced reference model for diagnosing similarly complex failures across modern vehicle
platforms.

Case Study #6 for Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram examines a complex real‑world failure involving cooling‑module
logic freeze triggered by micro‑arcing on supply lines. Symptoms emerged irregularly, with clustered faults
appearing across unrelated modules, giving the impression of multiple simultaneous subsystem failures. These
irregularities depended strongly on vibration, temperature shifts, or abrupt electrical load changes, making
the issue difficult to reproduce during initial diagnostic attempts. Technicians noted inconsistent sensor
feedback, communication delays, and momentary power‑rail fluctuations that persisted without generating
definitive fault codes. The investigation into cooling‑module logic freeze triggered by micro‑arcing on
supply lines required a multi‑layer diagnostic strategy combining signal‑path tracing, ground stability
assessment, and high‑frequency noise evaluation. Technicians executed controlled stress tests—including
thermal cycling, vibration induction, and staged electrical loading—to reveal the exact thresholds at which
the fault manifested. Using structured elimination across harness segments, module clusters, and reference
nodes, they isolated subtle timing deviations, analog distortions, or communication desynchronization that
pointed toward a deeper systemic failure mechanism rather than isolated component malfunction. Once
cooling‑module logic freeze triggered by micro‑arcing on supply lines was identified as the root failure
mechanism, targeted corrective measures were implemented. These included harness reinforcement, connector
replacement, firmware restructuring, recalibration of key modules, or ground‑path reconfiguration depending on
the nature of the instability. Post‑repair endurance runs with repeated vibration, heat cycles, and voltage
stress ensured long‑term reliability. Documentation of the diagnostic sequence and recovery pathway now
provides a vital reference for detecting and resolving similarly complex failures more efficiently in future
service operations.

Hands‑On Lab #1 for Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram focuses on electronic throttle response‑curve analysis under
voltage variation. This exercise teaches technicians how to perform structured diagnostic measurements using
multimeters, oscilloscopes, current probes, and differential tools. The initial phase emphasizes establishing
a stable baseline by checking reference voltages, verifying continuity, and confirming ground integrity. These
foundational steps ensure that subsequent measurements reflect true system behavior rather than secondary
anomalies introduced by poor probing technique or unstable electrical conditions. During the measurement
routine for electronic throttle response‑curve analysis under voltage variation, technicians analyze dynamic
behavior by applying controlled load, capturing waveform transitions, and monitoring subsystem responses. This
includes observing timing shifts, duty‑cycle changes, ripple patterns, or communication irregularities. By
replicating real operating conditions—thermal changes, vibration, or electrical demand spikes—technicians gain
insight into how the system behaves under stress. This approach allows deeper interpretation of patterns that
static readings cannot reveal. After completing the procedure for electronic throttle response‑curve analysis
under voltage variation, results are documented with precise measurement values, waveform captures, and
interpretation notes. Technicians compare the observed data with known good references to determine whether
performance falls within acceptable thresholds. The collected information not only confirms system health but
also builds long‑term diagnostic proficiency by helping technicians recognize early indicators of failure and
understand how small variations can evolve into larger issues.
Hands‑On Lab #2 for Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram focuses on electronic throttle control latency measurement. This
practical exercise expands technician measurement skills by emphasizing accurate probing technique, stable
reference validation, and controlled test‑environment setup. Establishing baseline readings—such as reference
ground, regulated voltage output, and static waveform characteristics—is essential before any dynamic testing
occurs. These foundational checks prevent misinterpretation caused by poor tool placement, floating grounds,
or unstable measurement conditions. During the procedure for electronic throttle control latency measurement,
technicians simulate operating conditions using thermal stress, vibration input, and staged subsystem loading.
Dynamic measurements reveal timing inconsistencies, amplitude drift, duty‑cycle changes, communication
irregularities, or nonlinear sensor behavior. Oscilloscopes, current probes, and differential meters are used
to capture high‑resolution waveform data, enabling technicians to identify subtle deviations that static
multimeter readings cannot detect. Emphasis is placed on interpreting waveform shape, slope, ripple
components, and synchronization accuracy across interacting modules. After completing the measurement routine
for electronic throttle control latency measurement, technicians document quantitative findings—including
waveform captures, voltage ranges, timing intervals, and noise signatures. The recorded results are compared
to known‑good references to determine subsystem health and detect early‑stage degradation. This structured
approach not only builds diagnostic proficiency but also enhances a technician’s ability to predict emerging
faults before they manifest as critical failures, strengthening long‑term reliability of the entire system.

Hands‑On Lab #3 for Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram focuses on oscilloscope-based ripple decomposition on ECU power
rails. This exercise trains technicians to establish accurate baseline measurements before introducing dynamic
stress. Initial steps include validating reference grounds, confirming supply‑rail stability, and ensuring
probing accuracy. These fundamentals prevent distorted readings and help ensure that waveform captures or
voltage measurements reflect true electrical behavior rather than artifacts caused by improper setup or tool
noise. During the diagnostic routine for oscilloscope-based ripple decomposition on ECU power rails,
technicians apply controlled environmental adjustments such as thermal cycling, vibration, electrical loading,
and communication traffic modulation. These dynamic inputs help expose timing drift, ripple growth, duty‑cycle
deviations, analog‑signal distortion, or module synchronization errors. Oscilloscopes, clamp meters, and
differential probes are used extensively to capture transitional data that cannot be observed with static
measurements alone. After completing the measurement sequence for oscilloscope-based ripple decomposition on
ECU power rails, technicians document waveform characteristics, voltage ranges, current behavior,
communication timing variations, and noise patterns. Comparison with known‑good datasets allows early
detection of performance anomalies and marginal conditions. This structured measurement methodology
strengthens diagnostic confidence and enables technicians to identify subtle degradation before it becomes a
critical operational failure.

Hands‑On Lab #4 for Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram focuses on PWM actuator slope‑integrity validation under
temperature shift. This laboratory exercise builds on prior modules by emphasizing deeper measurement
accuracy, environment control, and test‑condition replication. Technicians begin by validating stable
reference grounds, confirming regulated supply integrity, and preparing measurement tools such as
oscilloscopes, current probes, and high‑bandwidth differential probes. Establishing clean baselines ensures
that subsequent waveform analysis is meaningful and not influenced by tool noise or ground drift. During the
measurement procedure for PWM actuator slope‑integrity validation under temperature shift, technicians
introduce dynamic variations including staged electrical loading, thermal cycling, vibration input, or
communication‑bus saturation. These conditions reveal real‑time behaviors such as timing drift, amplitude
instability, duty‑cycle deviation, ripple formation, or synchronization loss between interacting modules.
High‑resolution waveform capture enables technicians to observe subtle waveform features—slew rate, edge
deformation, overshoot, undershoot, noise bursts, and harmonic artifacts. Upon completing the assessment for
PWM actuator slope‑integrity validation under temperature shift, all findings are documented with waveform
snapshots, quantitative measurements, and diagnostic interpretations. Comparing collected data with verified
reference signatures helps identify early‑stage degradation, marginal component performance, and hidden
instability trends. This rigorous measurement framework strengthens diagnostic precision and ensures that
technicians can detect complex electrical issues long before they evolve into system‑wide failures.

Hands‑On Lab #5 for Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram focuses on chassis grounding potential differential tracing under
load. The session begins with establishing stable measurement baselines by validating grounding integrity,
confirming supply‑rail stability, and ensuring probe calibration. These steps prevent erroneous readings and
ensure that all waveform captures accurately reflect subsystem behavior. High‑accuracy tools such as
oscilloscopes, clamp meters, and differential probes are prepared to avoid ground‑loop artifacts or
measurement noise. During the procedure for chassis grounding potential differential tracing under load,
technicians introduce dynamic test conditions such as controlled load spikes, thermal cycling, vibration, and
communication saturation. These deliberate stresses expose real‑time effects like timing jitter, duty‑cycle
deformation, signal‑edge distortion, ripple growth, and cross‑module synchronization drift. High‑resolution
waveform captures allow technicians to identify anomalies that static tests cannot reveal, such as harmonic
noise, high‑frequency interference, or momentary dropouts in communication signals. After completing all
measurements for chassis grounding potential differential tracing under load, technicians document voltage
ranges, timing intervals, waveform shapes, noise signatures, and current‑draw curves. These results are
compared against known‑good references to identify early‑stage degradation or marginal component behavior.
Through this structured measurement framework, technicians strengthen diagnostic accuracy and develop
long‑term proficiency in detecting subtle trends that could lead to future system failures.
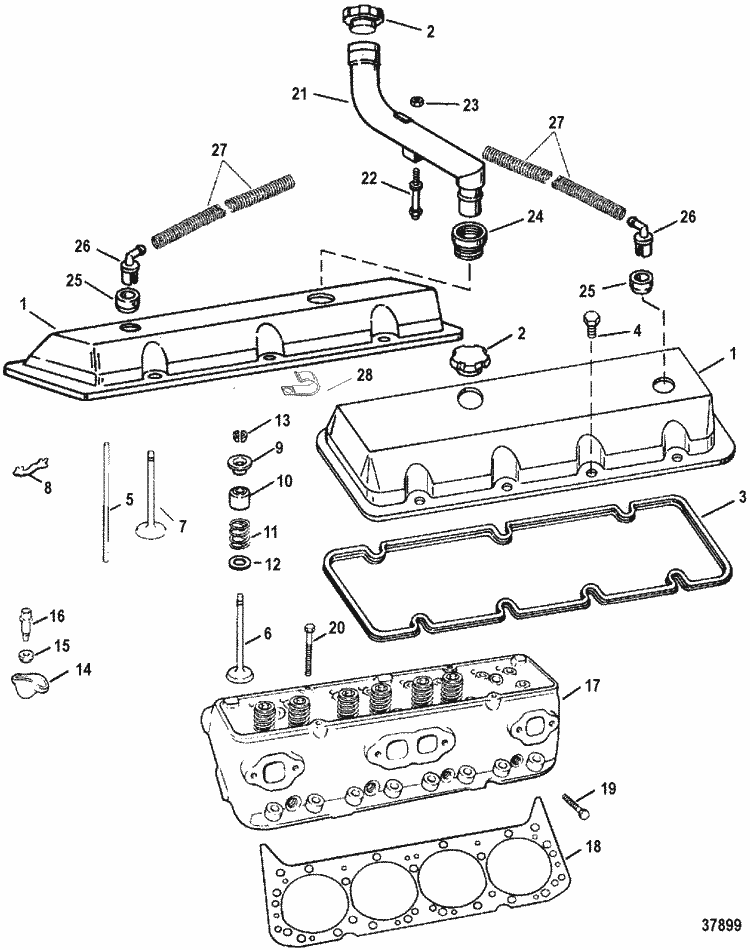
Hands‑On Lab #6 for Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram focuses on oscilloscope‑guided crank/cam phase coherence
analysis. This advanced laboratory module strengthens technician capability in capturing high‑accuracy
diagnostic measurements. The session begins with baseline validation of ground reference integrity, regulated
supply behavior, and probe calibration. Ensuring noise‑free, stable baselines prevents waveform distortion and
guarantees that all readings reflect genuine subsystem behavior rather than tool‑induced artifacts or
grounding errors. Technicians then apply controlled environmental modulation such as thermal shocks,
vibration exposure, staged load cycling, and communication traffic saturation. These dynamic conditions reveal
subtle faults including timing jitter, duty‑cycle deformation, amplitude fluctuation, edge‑rate distortion,
harmonic buildup, ripple amplification, and module synchronization drift. High‑bandwidth oscilloscopes,
differential probes, and current clamps are used to capture transient behaviors invisible to static multimeter
measurements. Following completion of the measurement routine for oscilloscope‑guided crank/cam phase
coherence analysis, technicians document waveform shapes, voltage windows, timing offsets, noise signatures,
and current patterns. Results are compared against validated reference datasets to detect early‑stage
degradation or marginal component behavior. By mastering this structured diagnostic framework, technicians
build long‑term proficiency and can identify complex electrical instabilities before they lead to full system
failure.

Checklist & Form #1 for Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram focuses on PWM actuator functional verification checklist.
This verification document provides a structured method for ensuring electrical and electronic subsystems meet
required performance standards. Technicians begin by confirming baseline conditions such as stable reference
grounds, regulated voltage supplies, and proper connector engagement. Establishing these baselines prevents
false readings and ensures all subsequent measurements accurately reflect system behavior. During completion
of this form for PWM actuator functional verification checklist, technicians evaluate subsystem performance
under both static and dynamic conditions. This includes validating signal integrity, monitoring voltage or
current drift, assessing noise susceptibility, and confirming communication stability across modules.
Checkpoints guide technicians through critical inspection areas—sensor accuracy, actuator responsiveness, bus
timing, harness quality, and module synchronization—ensuring each element is validated thoroughly using
industry‑standard measurement practices. After filling out the checklist for PWM actuator functional
verification checklist, all results are documented, interpreted, and compared against known‑good reference
values. This structured documentation supports long‑term reliability tracking, facilitates early detection of
emerging issues, and strengthens overall system quality. The completed form becomes part of the
quality‑assurance record, ensuring compliance with technical standards and providing traceability for future
diagnostics.

Checklist & Form #2 for Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram focuses on harness insulation‑breakdown risk assessment. This
structured verification tool guides technicians through a comprehensive evaluation of electrical system
readiness. The process begins by validating baseline electrical conditions such as stable ground references,
regulated supply integrity, and secure connector engagement. Establishing these fundamentals ensures that all
subsequent diagnostic readings reflect true subsystem behavior rather than interference from setup or tooling
issues. While completing this form for harness insulation‑breakdown risk assessment, technicians examine
subsystem performance across both static and dynamic conditions. Evaluation tasks include verifying signal
consistency, assessing noise susceptibility, monitoring thermal drift effects, checking communication timing
accuracy, and confirming actuator responsiveness. Each checkpoint guides the technician through critical areas
that contribute to overall system reliability, helping ensure that performance remains within specification
even during operational stress. After documenting all required fields for harness insulation‑breakdown risk
assessment, technicians interpret recorded measurements and compare them against validated reference datasets.
This documentation provides traceability, supports early detection of marginal conditions, and strengthens
long‑term quality control. The completed checklist forms part of the official audit trail and contributes
directly to maintaining electrical‑system reliability across the vehicle platform.

Checklist & Form #3 for Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram covers EMI shielding‑layout compliance checklist. This
verification document ensures that every subsystem meets electrical and operational requirements before final
approval. Technicians begin by validating fundamental conditions such as regulated supply voltage, stable
ground references, and secure connector seating. These baseline checks eliminate misleading readings and
ensure that all subsequent measurements represent true subsystem behavior without tool‑induced artifacts.
While completing this form for EMI shielding‑layout compliance checklist, technicians review subsystem
behavior under multiple operating conditions. This includes monitoring thermal drift, verifying
signal‑integrity consistency, checking module synchronization, assessing noise susceptibility, and confirming
actuator responsiveness. Structured checkpoints guide technicians through critical categories such as
communication timing, harness integrity, analog‑signal quality, and digital logic performance to ensure
comprehensive verification. After documenting all required values for EMI shielding‑layout compliance
checklist, technicians compare collected data with validated reference datasets. This ensures compliance with
design tolerances and facilitates early detection of marginal or unstable behavior. The completed form becomes
part of the permanent quality‑assurance record, supporting traceability, long‑term reliability monitoring, and
efficient future diagnostics.

Checklist & Form #4 for Chevy 454 Engine Belt Diagram 2026 Belt Diagram documents noise‑resilience audit for mixed‑signal pathways.
This final‑stage verification tool ensures that all electrical subsystems meet operational, structural, and
diagnostic requirements prior to release. Technicians begin by confirming essential baseline conditions such
as reference‑ground accuracy, stabilized supply rails, connector engagement integrity, and sensor readiness.
Proper baseline validation eliminates misleading measurements and guarantees that subsequent inspection
results reflect authentic subsystem behavior. While completing this verification form for noise‑resilience
audit for mixed‑signal pathways, technicians evaluate subsystem stability under controlled stress conditions.
This includes monitoring thermal drift, confirming actuator consistency, validating signal integrity,
assessing network‑timing alignment, verifying resistance and continuity thresholds, and checking noise
immunity levels across sensitive analog and digital pathways. Each checklist point is structured to guide the
technician through areas that directly influence long‑term reliability and diagnostic predictability. After
completing the form for noise‑resilience audit for mixed‑signal pathways, technicians document measurement
results, compare them with approved reference profiles, and certify subsystem compliance. This documentation
provides traceability, aids in trend analysis, and ensures adherence to quality‑assurance standards. The
completed form becomes part of the permanent electrical validation record, supporting reliable operation
throughout the vehicle’s lifecycle.
