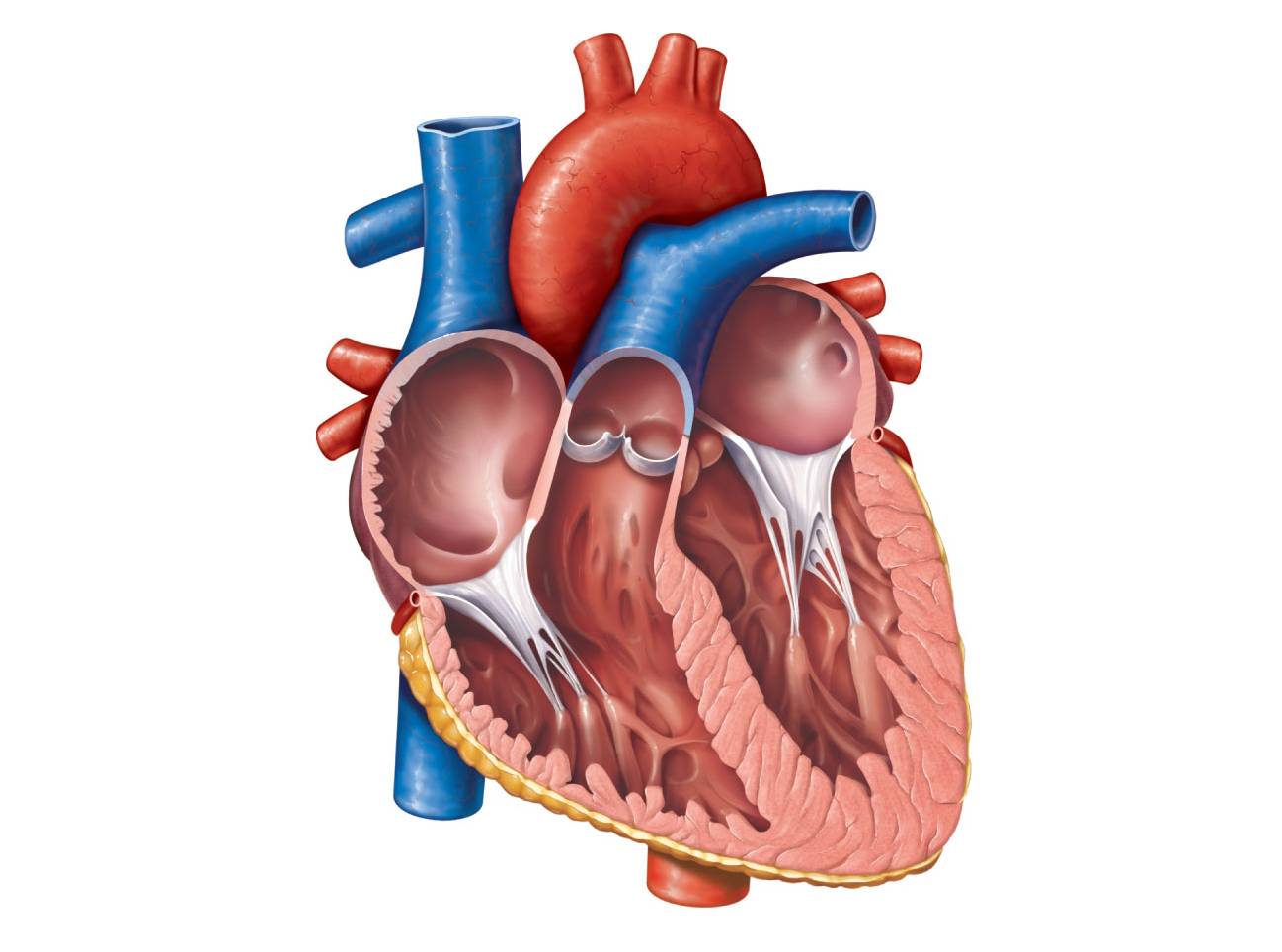
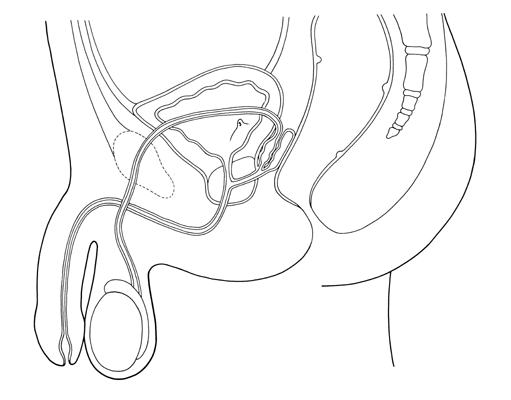
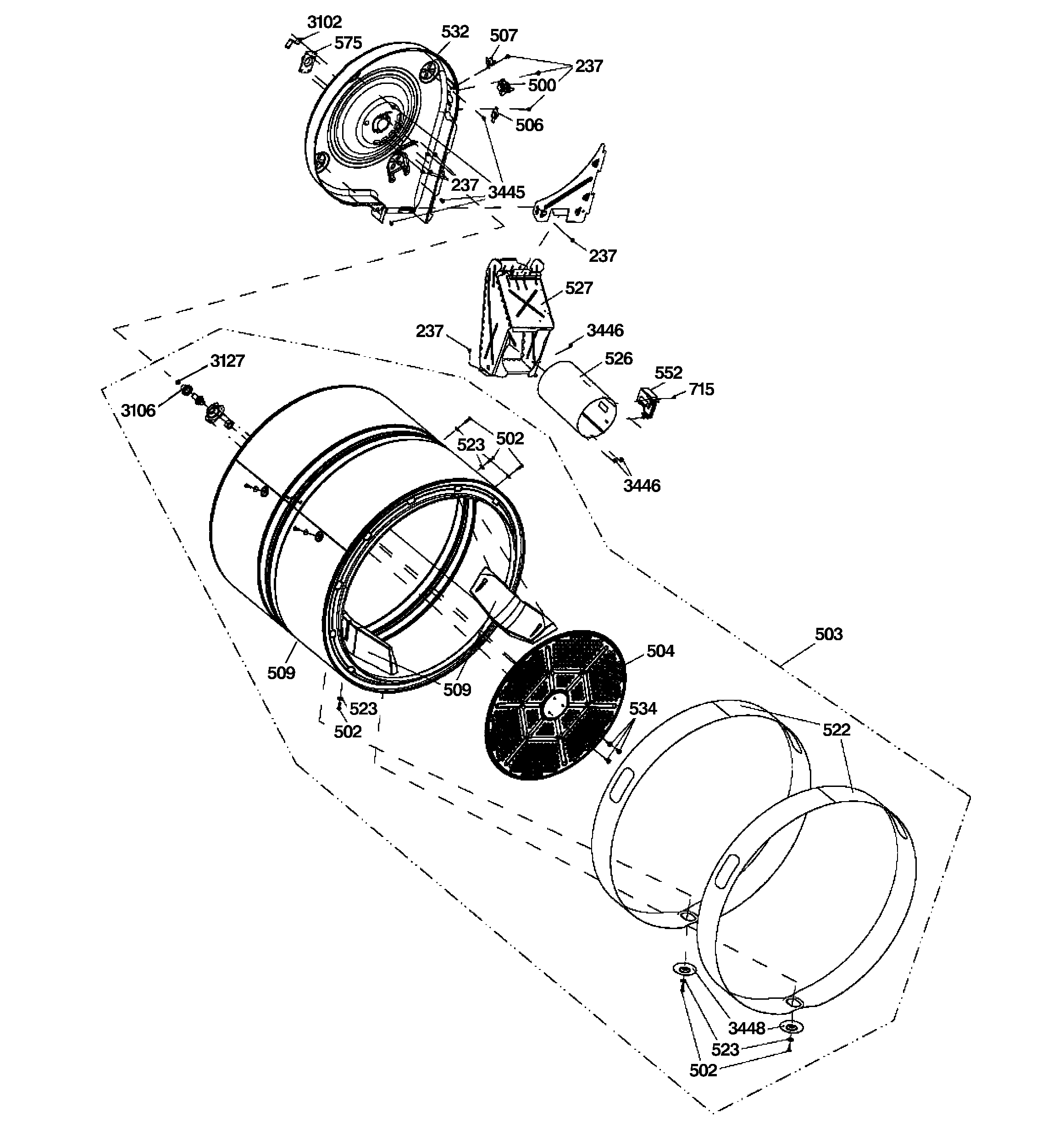
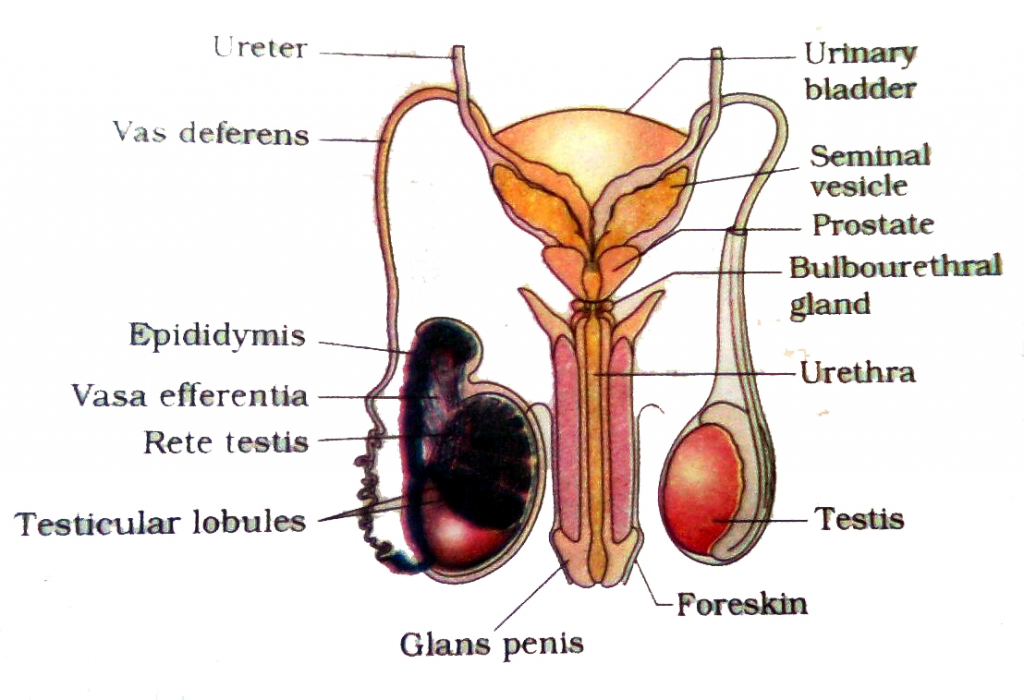
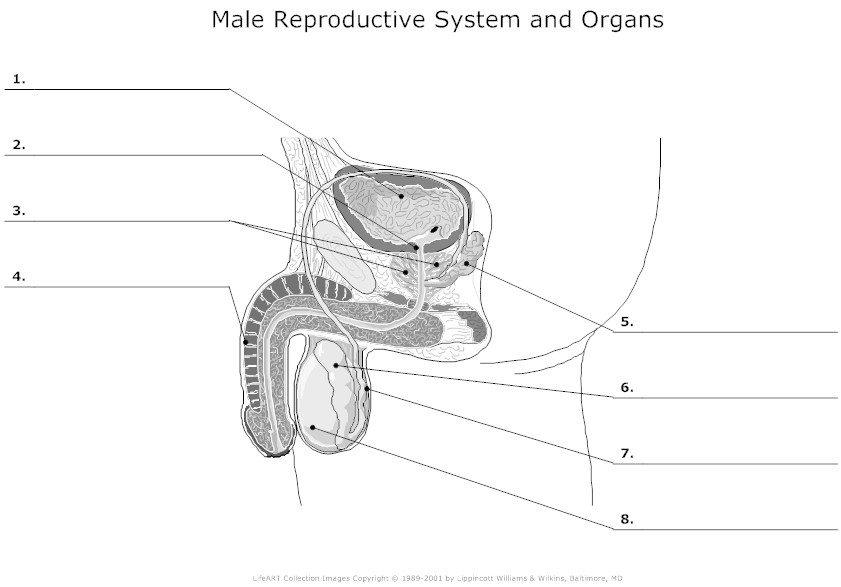
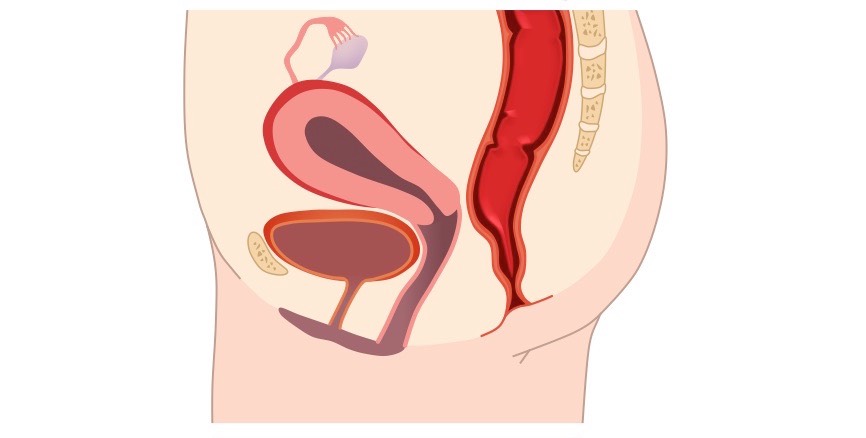
Wiring systems are the unseen networks that support every modern machine, from vehicles to factories to home appliances. This technical overview is written for both trained troubleshooters and dedicated hobbyists who want to understand the logic, structure, and purpose behind wiring diagrams. Instead of treating lines and labels as guesswork or just copying colors wire to wire, you will learn how electricity truly flows how current moves through conductors, how voltage behaves under load, and how resistance affects performance in real circuits. This is the core promise of the Male Reproductive System Diagram Unlabeled project, published for Diagram Unlabeled in 2026 under http://wiringschema.com and served from https://http://wiringschema.com/male-reproductive-system-diagram-unlabeled/WIRINGSCHEMA.COM.
The foundation of any wiring system begins with three fundamental principles: power distribution, establishing a clean reference path, and overcurrent protection. These elements determine how safely and efficiently current travels through the system. Power distribution ensures that each component receives the voltage it requires; grounding provides a stable return path to prevent buildup of unwanted electrical potential; and protection using fuses, breakers, or electronic current monitoring prevents overloads that could damage equipment or even start fires. Together, these three pillars form the backbone of every schematic you will ever read, whether you are working on automotive harnesses, industrial panels, or consumer electronics in Diagram Unlabeled.
Interpreting wiring diagrams is not just about following lines on paper. It is about visualizing what actually happens in physical hardware. A wire labeled 12V feed is more than a symbol it represents a conductor that delivers energy from the source to sensors, relays, and modules. A ground symbol is not decoration; it is the path that stabilizes voltage differences across the entire system. Once you learn to connect these abstract drawings to physical components, wiring diagrams transform from confusion into clarity. At that moment, the schematic stops being a mystery and becomes a map of intentional design.
A well-designed wiring manual does not only explain where wires go. It teaches you how to reason through electrical behavior. If a headlight flickers, the cause may not be the bulb at all. The issue could be poor grounding, corroded connectors, or an intermittent open circuit somewhere upstream. By tracing the schematic from the power source, through the switch and relay, and into the load, you can logically isolate the fault instead of guessing. That is the difference between replacing parts and solving problems. This diagnostic mindset is exactly what separates a casual trial-and-error approach from professional workflow.
Throughout this Male Reproductive System Diagram Unlabeled guide, you will explore how different systems communicate and share resources. In automotive wiring, for example, a single control module may coordinate lighting, wipers, climate elements, and sensor inputs at the same time. Each function relies on shared grounds, shared reference voltages, and sometimes even shared data lines. Industrial systems extend this idea further with structured bus communication programmable logic controllers, safety relays, emergency stop loops, and feedback sensors all talking together on a defined network. Regardless of the industry, the underlying logic stays consistent: energy flows from source to load, that energy is controlled by switches or transistors, it is protected by fuses, and the entire circuit is stabilized through reliable grounding.
Tools convert theory into proof. A digital multimeter (DMM) lets you measure voltage, resistance, and continuity so you can confirm whether a circuit is actually intact. An oscilloscope shows real-time waveforms that reveal how sensors and actuators communicate using analog levels or pulse-width-modulated signals. A clamp meter helps you observe current flow without disconnecting anything. Learning to use these instruments correctly lets you verify that the circuit is behaving the way the schematic says it should. If the diagram predicts 12 volts at a junction and you only read 9.4 under load, you immediately know there is resistance, loss, or heat somewhere between source and that point.
Safety is another critical pillar of wiring knowledge, and it applies equally to professionals and hobbyists in Diagram Unlabeled and beyond. Always disconnect the power source before probing exposed conductors. Use insulated tools when working near high current. Keep in mind that even so-called low voltage systems can deliver dangerous current in a fault state. Never bypass protective devices just to test quickly, and never substitute a higher fuse rating as a shortcut. The small habit of respecting safety rules prevents expensive failures, personal injury, and in some cases fire. Document what you did. Label what you touched. Make the next inspection easier even if the next person working on it is future you.
As you gain experience reading diagrams, you start to develop an intuitive understanding of how electrical systems make decisions. You will begin to see how sensors convert physical inputs position, pressure, temperature, motion into signals. You will see how actuators translate those signals into mechanical response. You will see how controllers coordinate the entire process using logic, timing, and protection. At that point, every individual wire stops being just a wire and instead becomes part of a conversation: a silent digital and electrical language that tells machines what to do, when to do it, and how long to keep doing it.
In advanced applications like automated manufacturing lines, energy storage systems, or electric vehicles, schematics become even more critical. These systems fuse mechanical components, embedded electronics, and software-based control into one interdependent structure. Reading those diagrams requires patience and disciplined thinking, but the reward is huge. Once you understand the diagram, you gain the ability to diagnose faults that appear random to everyone else. You do not just repair after failure you start predicting failure before it happens.
Ultimately, the purpose of this Male Reproductive System Diagram Unlabeled manual is to help you see wiring systems not as tangled webs of copper, but as deliberate architectures of control and power. By understanding how energy travels, how signals interact, and how each connector, fuse, relay, switch, and ground point plays a role, you gain the confidence to design, troubleshoot, and improve systems safely. Every line on a wiring diagram tells a story of intent a story about power, stability, protection, and responsibility. When you learn to read that story, you are no longer guessing. You are operating with clarity, you are working with discipline, and you are seeing the machine the way the designer saw it on day one in 2026 at http://wiringschema.com.
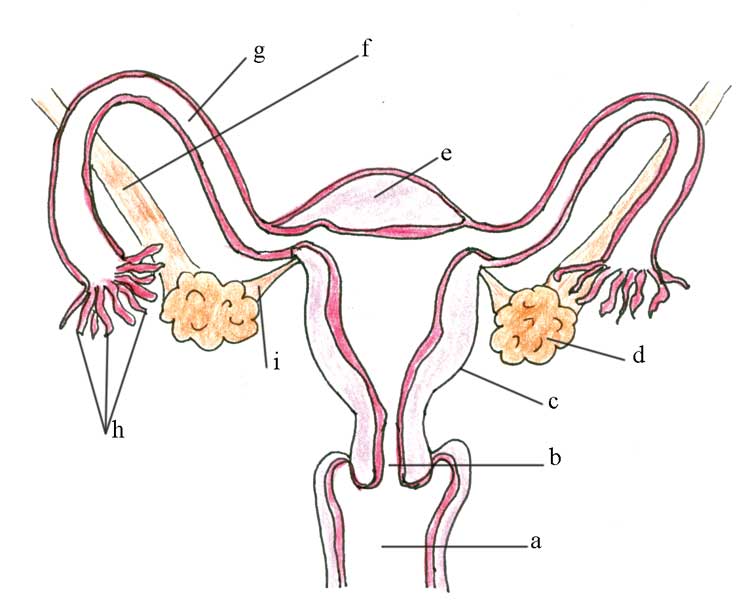
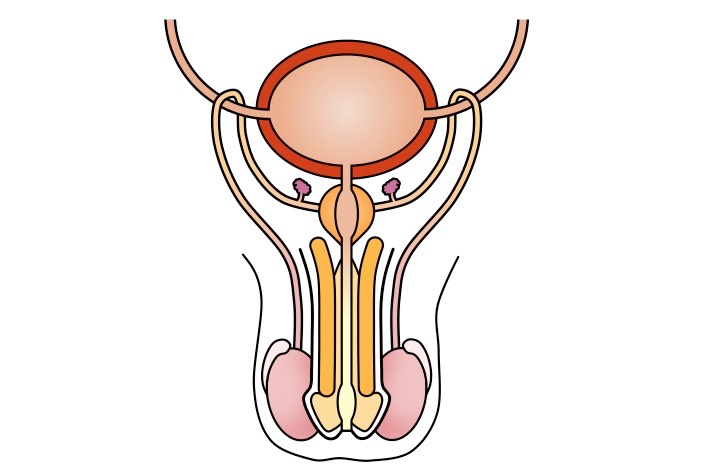
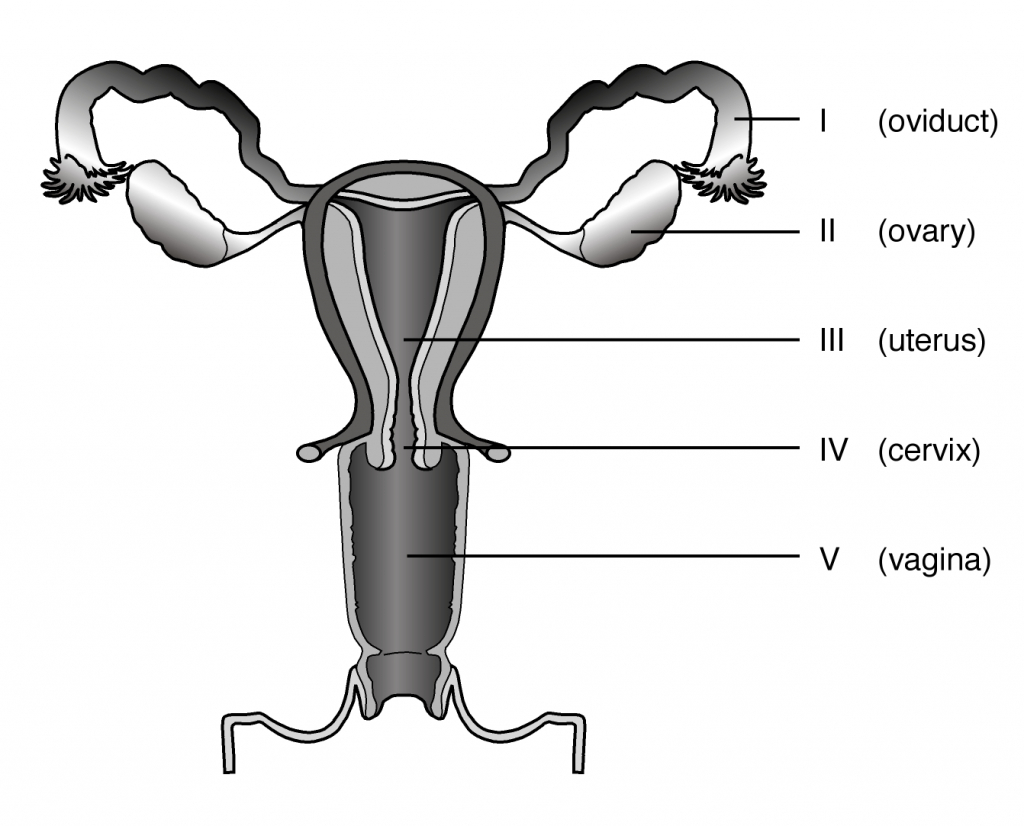


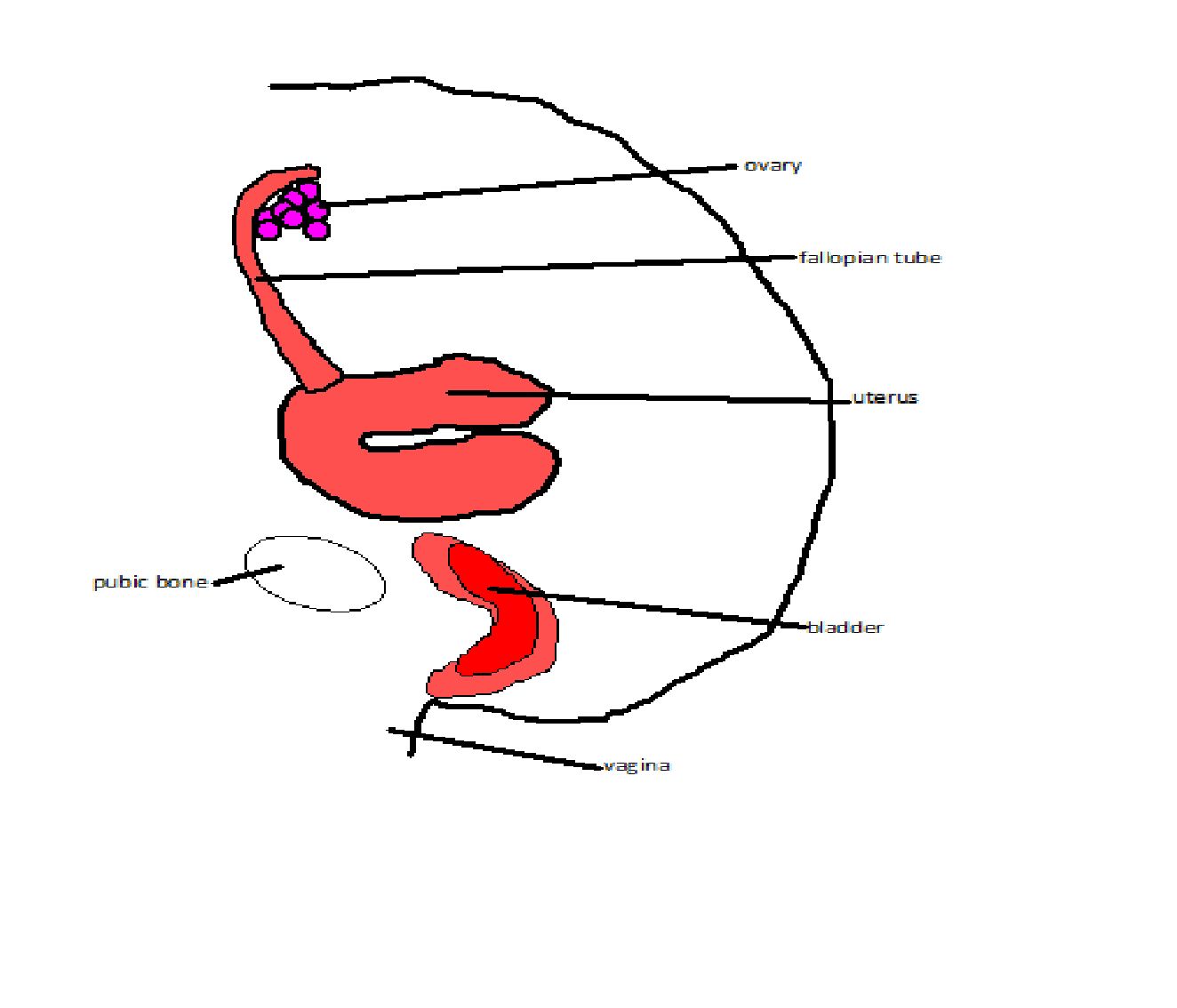


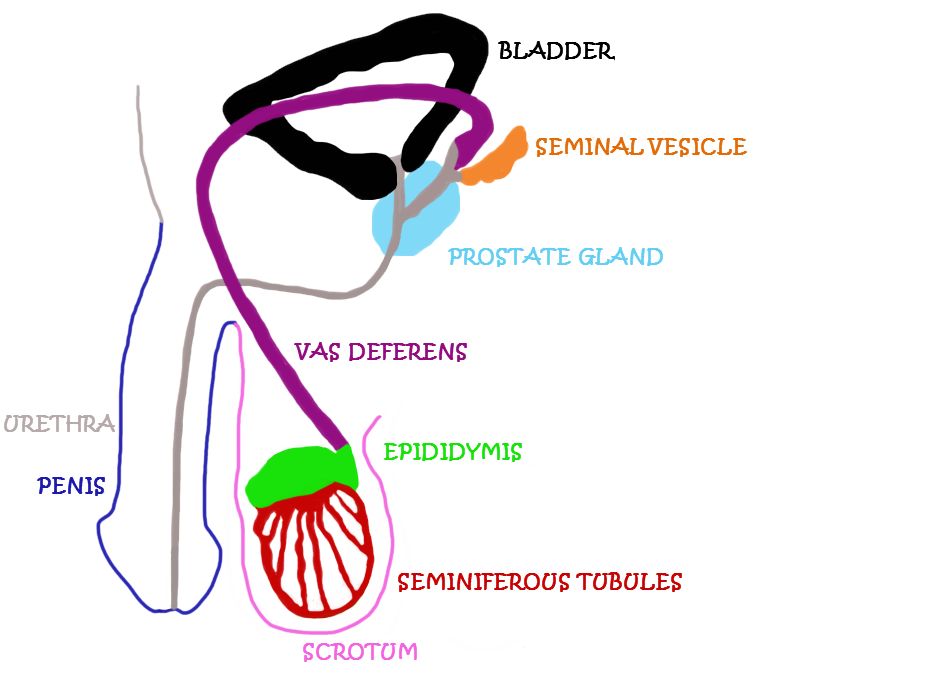











.jpg)